In the News

In the race to an all-optical AI data center, a major player has now placed a bet on a different horse. Semiconductor manufacturing giant TSMC announced that it will work with Sunnyvale startup Avicena to produce microLED-based interconnects. The technology is a pragmatic twist on replacing electrical connections with optical ones to meet the high needs of communication among an increasing number of GPUs in a low cost, energy efficient way.

GazettaByte — TSMC, the leading semiconductor foundry, will make the photo-detectors used for Avicena Tech’s microLED optical interconnect technology.
Avicena is developing an optical interface that uses hundreds of parallel fibre links – each link comprising a tiny LED tranmitter and a silicon photo-detector receiver – to deliver terabit-per-second (Tbps) data transfers.


Optical Connections
Multi-terabit μLED based interconnects: Unleashing the potential of HPC and AI

Photonics Spectra
Product News: Chiplet Interconnect
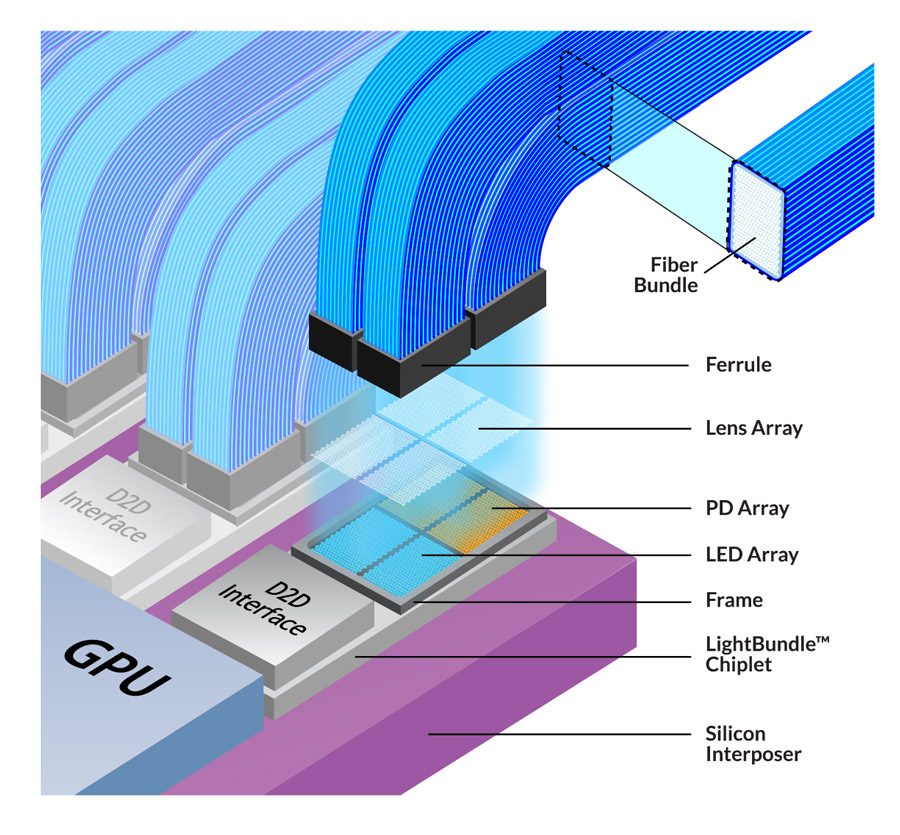
Optical Connections
OFC 2024: Avicena debuts scalable Sub-pJ/bit chiplet

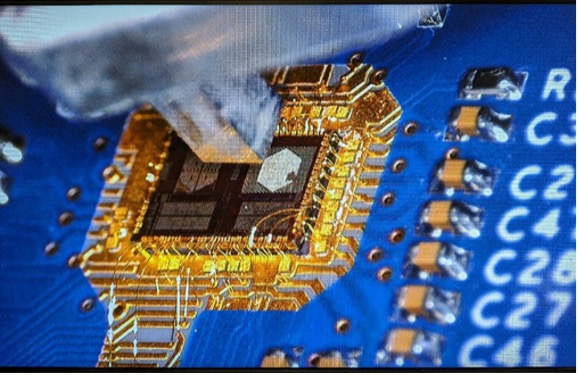
Optical Connections
Avicena debuts world’s smallest 1Tbps optical transceiver

Lightcounting
Photonics-Enabled Disaggregated Computing
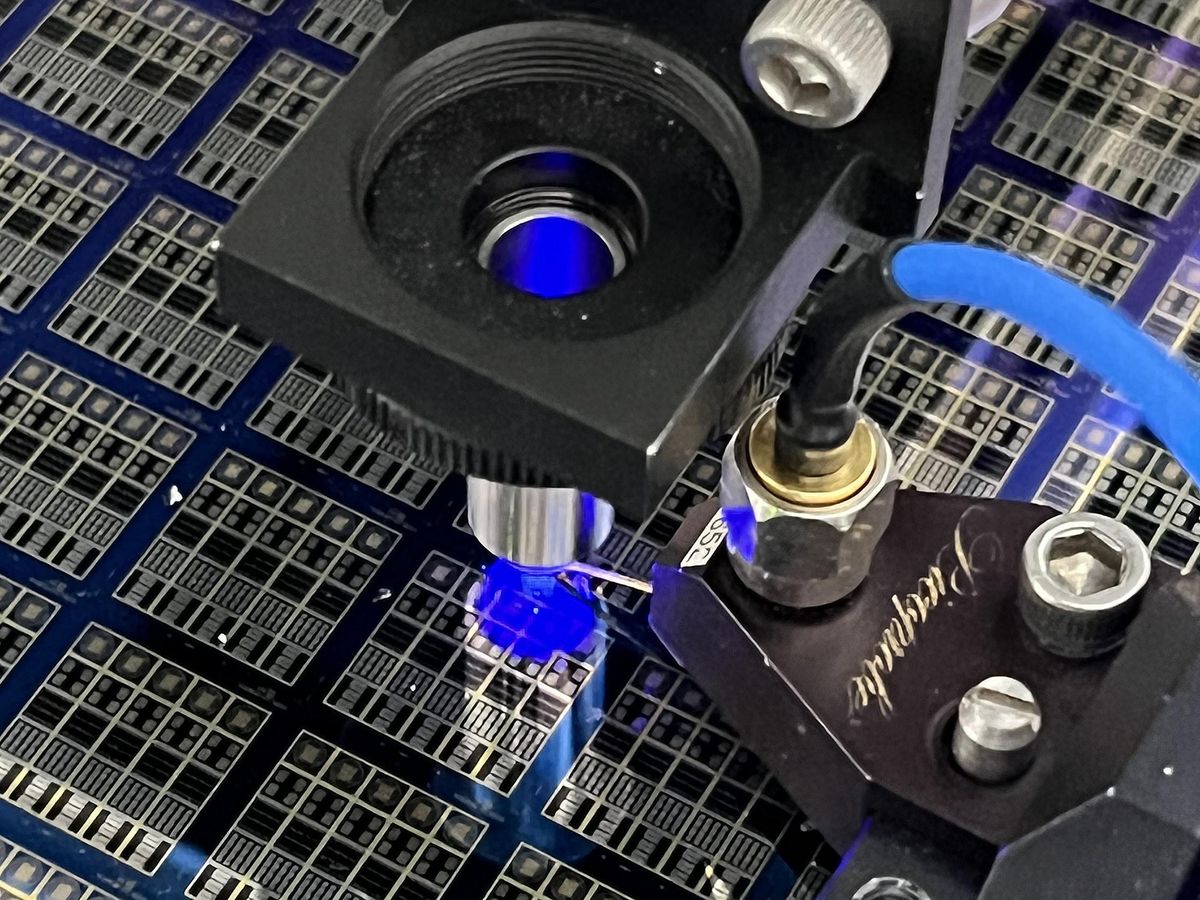
IEEE Spectrum

